B Rapa
Rapa, e.g., yellow sarson, are self-compatible.

B rapa. Rapa (A r A r genome) and B. Chinensis - チンゲンサイ (シャクシナ、タイサイ) B. The leaves of B.
2 a, the rosette leaves of B. This plant is widely distributed in Europe, Central Asia and the Near East, and is commonly cultivated in the regions of Tibet, Xinjiang, and Sichuan in China.8 – 10 B. Rapa Also referred to as Polish canola, it is the less commonly grown species of canola currently grown in Canada.
Hypothesis Purple and green stem colors are inherited through simple dominance with purple being recessive and green being dominant. It is believed to have originated relatively late in Europe, probably as a cross between wild cabbage (B. Genomes in NCBI/EMBL Pan-genomes From the Edwards' lab B.
The region of several kilobases (∼40–60 kb) from SP6 to SP2 , including self-incompatibility-related genes and some adjacent genes in Brassica rapa , has high nucleotide diversity due to the hitchhiking effect, and therefore we call this region. Amplexicaulis - ハナナ ( wikidata ) ( 山東菜 ) B. All of these responses were dependent on nitrogen and polar auxin transport.
As shown in Fig. Chinensis varieties do not form heads and have green leaf blades with lighter bulbous bottoms instead, forming a cluster reminiscent of mustard greens. Two weeks later, the seedlings were transplanted into the field at the Songjiang Farm Station of SIPPE in early September.
Rapa, turnip, cultivated for its tuberous taproot, sometimes escapes as a weed. Rapid Assessment of Physical Activity (RAPA) The Rapid Assessment of Physical Activity (RAPA) questionnaire was designed to provide clinicians with a tool for quickly assessing the level of physical activity of their older adult patients. We identified 60 SET(HKMTases), 53 JmjC, and 4 LSD(HDMases) genes in B.
The lobed rosette leaves of B. The Zeitschrift Fur Naturforschung Section C - a Journal of Biosciences report. Napus Also referred to as Argentine canola, it is the species of canola currently commonly grown in Canada.
Ready to pasture in 6 to 8 weeks. Oleifera DC., Turnip rape, grown as a fodder crop, has larger reddishbrown seeds and non-tuberous taproot. The efficacy of any such measure depends on hybrid numbers within the legislative region over the life-span of the GM cultivar.
Re-sequencing and SNPs >Fifty two B. Rapa educational model system is available to aid in student education in areas of genetics, evolution, and genomic sciences. (1) the effects of exogenous glucosinolates on Lolium root length depended on the presence of myrosinase.
Olearacea), with stems that grow. Oleracea give us several important vegetables, including broccoli, cauliflower, and brussels sprouts. Sylvestris (L.) Janchen (B.
Two-species hybrids, formed between these Brassica, are also important crops. Napus leaves partially clasp the stem while those of B. Glabra Regel - カブ(アジア系) 、 テンノウジカブラ B.
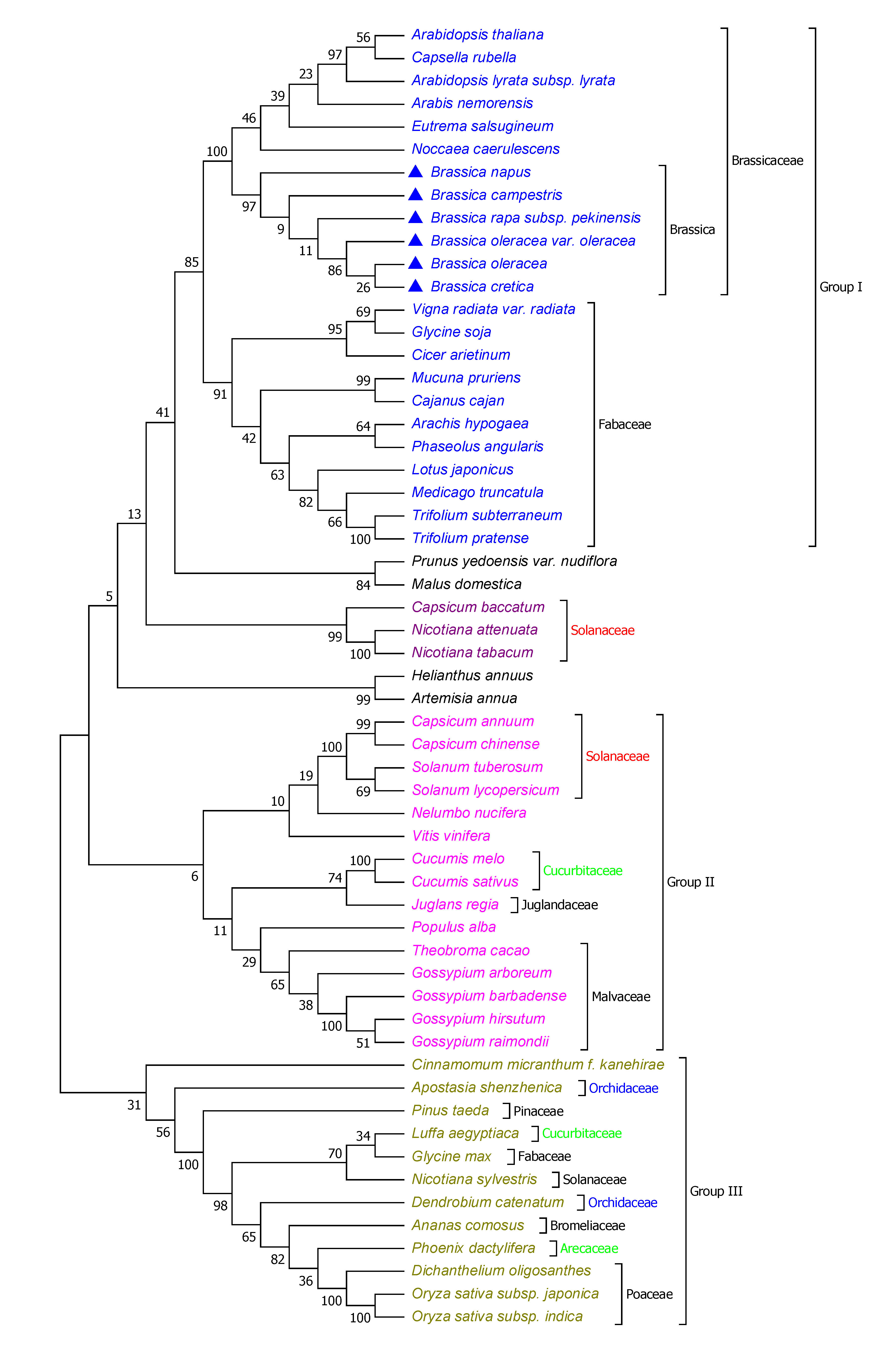
Brassica rapa is an important oilseed and vegetable crop species and is the A subgenome donor of two important oilseed Brassica crops, Brassica napus and Brassica juncea. Oleracea) and turnip mustard (B. Forms the basis for waste legislation, reporting obligations and the notification of.
Rapa varieties had a grassy-green color and a thin oval shape. Brassica rapa infested some of the freeway interchanges and was probably the primary species in the freeway median. Fast Plants are a special form of the species Brassica rapa (Wisconsin Fast Plants), a member of the mustard or cabbage family Cruciferae.
Napus, AACC, 2n=38) is an economically important oilseed crop which provides approximately 13-16% of the vegetable oil globally. Napus occurred in two field experiments (frequency approximately 7%) and in wild populations in commercial fields (approximately 13.6%). The ancestor of rapeseed and swede is not known to grow ferally.
Rapa L.) and two mustard species (B. The heading time is important for high quality and yield of these crops. In Canada, these species are commonly referred to as volunteer canola, while feral populations of B.
Bre) was used in this study. This form is dealt with on this record. If you cross B.
Oleracea, one with B. Napus genomes and 4.3 million SNPs (15, NAM consortium, Germany). Rapa are native to Eurasia.
Oilseed subspecies (oleifera) of Brassica rapa may have been domesticated several times from the Mediterranean to India, starting as early as 00 BC. In response to elevated levels of CO2, B. The domain composition analysis subcategorized them into seven and nine subgroups, respectively.
The loci were identified using a combination of 5 RFLP and 25 PCR-based markers. Crucifers are distinguished by characteristic flowers with four petals in the form of a cross or crucifix. Rapa, formerly known as B.
Can be grazed multiple times. The seeds were sown in a greenhouse on August 8, 14. Not a gibberellic-deficient mutant.
Chinensis) is a type of Chinese cabbage. Kaber, four with Raphanus sativus, and two with R. Though carrot (Daucus carota), radish (Raphanus sativus), turnip (Brassica rapa), garden beet (Beta vulgaris), parsnip (Pastinaca sativa), and rutabaga (Brassica napus var.
Field mustard is an upright winter annual or biennial that is a member of the mustard family (Brassicaceae). Field mustard is a weed or ruderal in much of. My first time composing a “Crossover” Concerto for the trumpet world, called “Tales of the Orient Expre.
Instead, the breakdown products of the glucosinolate–myrosinase reaction appeared to function as allelopathic agents, which may benefit B. Here, we report on a novel system using individual kernel analyses for the qualitative detection of RT73 B. Although seed size (SZ), seed color (SC), and oil content (OC) substantially affect seed yield and quality, the mechanisms regulating these traits in Brassica crops remain unclear.
Oleracea, you get B. PLANTS Characteristics Data Fields and Definitions for more than 100 Characteristics. Rapa from a.
The turnip then spread east to China, and reached Japan by 700 AD. Chinensis varieties are popular in southern China and Southeast Asia.Being winter-hardy, they are increasingly. She is affiliated with numerous hospitals, including Twin Cities Hospital (FL) and more.
Bok choy (American English), pak choi (British English), or pok choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Oleracea and Arabidopsis thaliana, were divided into 6 subfamilies containing 16 A r-A n and 11 C o-C n reliable orthologous pairs. Edible turnips were possibly first cultivated in northern Europe, and were an important food in ancient Rome.
Pekinensis), Brussels sprouts (B. Plants grow 1 to 3 (or 4) ft tall from a sometimes fleshy, enlarged taproot, with a many-branched stem. Rapa is a diploid but plant breeders have developed some tetraploid crops, notably fodder turnips and turnip rapes.
This mutant was crossed with ‘Tobin’ to derive F 4 lines having <6% total PUFA and oleic acid concentrations >87%. Online Only This product is not available in our print catalog. Rapa seedlings showed increases in hypocotyl length, shoot and root fresh weight, and the number of lateral roots.
Rapa, three with B. Of the 44 sites surveyed, 34 were infested with B. Based on phylogenetic analysis, 114 Hsp70 proteins derived from B.
Rapa has been used as a medicine and food plant;. The buds somewhat resemble broccoli, but do not form a large head.Rapini is known for its slightly bitter taste, and is particularly associated with Mediterranean cuisine. Other forms of Brassica rapainclude turnips, Chinese cabbage, pak choi and canola.
Forage for hogs, sheep, and young stock. The most promising mutant identified from 4 734 M 2 seeds of B. Here, we use Brassica rapa as a crop model to test for conservation of the phytochrome-carbon network.
Read real user reviews of over 1,000,000 Properties worldwide. Plants exist as basal rosettes until flowering stems develop at maturity, usually in the second year. Brassica rapa (Wisconsin Fast Plants®), Petite Seed, Pack of 50.
Problem What are the inheritance patterns of the stem colors colors purple and green in B. We present a national assessment of hybridization between rapeseed ( Brassica napus ) and B. Napus is originated in the Mediterranean.
A detailed genetic linkage map of Brassica rapa has been constructed containing 545 sequence-tagged loci covering 1287 cM, with an average mapping interval of 2.4 cM. Rapa is also called (NIUMA), MANJING and YUANJEN in Tibet and used for the treatment of all kinds of poisons, including. Napus are hairless, smooth, fleshy and bluish-green in colour while those of B.
Napus varieties had grayish color, thicker lobed shape, waxy surface, and bold white veins (Fig. Wisconsin Fast Plants® Petite (Petite) - Recessive;. The herbicide-tolerant genetically modified Roundup Ready canola (Brassica napus) line RT73 has been approved worldwide for use in animal feed and human food.
Napus, one with B. Napus varieties were jagged and notched deep to the midrib. Brassica (/ ˈ b r æ s ɪ k ə /) is a genus of plants in the mustard family (Brassicaceae).The members of the genus are informally known as cruciferous vegetables, cabbages, or mustard plants.Crops from this genus are sometimes called cole crops—derived from the Latin caulis, denoting the stem or stalk of a plant.
In self-incompatibility, a number of S haplotypes are maintained by frequency-dependent selection, which results in trans -specific S haplotypes. Brassica rapa is primarily a self-incompatible species, as are the other diploid brassicas, although some types of B. Measures blocking hybridization would prevent or reduce biotic or environmental change caused by gene flow from genetically modified (GM) crops to wild relatives.
We collected seeds from a pair of B. RFLP probes were derived from 359 B. Plants of reduced height (5 to 15 cm);.
Different strains of B. The self-incompatibility (SI) in cruciferous species is of the homomorphic sporophytic type determined by a single S locus. Jessica B Rapa specializes in physician assistant and has over 10 years of experience in the field of medicine.
Duplication analysis for paralogous pairs of SET and JmjC (eight and nine pairs, respectively) exhibited variation. Rapa and 26 Arabidopsis. Succulent plant related to cabbage Persists well after the first frost but rarely overwinters in Upper Midwest Earlier maturity and greater shatter resistance Well adapted to short-season growing areas Best Use:.
This is the wild form of the species. No Expedia cancellation fee. Rapa have been grown commercially for their seed oil content in western Canada since the middle of the last century and volunteer populations are common in fields.
Brassica napus and B. Rapa EST clones and amplification products of 11 B. The base of B.
Rapa gives us turnips, and B. Napobrassica) are major root crops of the temperate region, there are distinct tropical types of the first three crops which are grown extensively in tropical Asia. Napus, the species that gives.
Rapa are referred to as birdrape.Brassica napus and B. Oleracea (C o C o genome), respectively. The rosette leaves of B.
The effect of late season insect infestation on seed yield, yield components, oil content and oil quality of two canola species (Brassica napus L. Napus have not been approved in Japan. Jessica B Rapa has a medical practice at 4592 East Highway , Niceville, FL.
Click on the link and you can browse the FPsc genome, conduct BLAST searches, or just revel in the fact that this amazing resource—a more-or-less complete description of each base-pair that comprises the ~550,000,000 (that’s 550 Mbp) genome of our B. The wild turnip is a common weed of seed production regions and can pose considerable risk A review of Brassica species. Repeats annotation from the Edwards Lab.
SUBSPECIFIC or CULTIVAR GROUPS - chinensis (pak choi), pekinensis (Chinese cabbage), rapifera (turnip), oleifera (turnip rape), etc. Rapa now preferred terminology) chromosome number 2n = subspecific groups. THIS — is something I’m very proud to share with you.
Gemmifera) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa) comprise extremely incurved leaves that are edible vegetable products. Campestris, shows considerable variation in growth form and characteristics across the many cultivars, this species has, in general, a flat or globose root (in the case of turnips) without an elongated crown (as found in the rutabagas and kohlrabi, which are derived from B. Jessica B Rapa is a Physician Assistant Specialist in Niceville, Florida.
Rapa plants in competition, thereby reducing net costs of chemical defense. Keep it cut or grazed down so it doesn’t get tall and woody. Nigra gives us black mustard.
See wild turnip), but it is unclear if swede was a prototype of rapeseed, or vice versa. However, RT73 Brassica rapa lines derived from interspecific crosses with RT73 B. The species was actually named for the cultivated garden turnip with its edible swollen tap root.
Rapa L. Seed yield. The leafy heads of cabbage (Brassica oleracea), Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapassp. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to find the inheritance pattern for stem color in B.
Brassica rapa is an ideal organism for studying genetics because of this short life cycle. Napus, the buds are borne above the open florets while in B. 11.9% linoleic and 8.6% linolenic acid in the original cultivar.
It does not have a swollen root and is closest to the forms grown for their oil-rich seeds. The higher frequency in commercial fields was most likely due to greater distance between B. She graduated with honors in 10.
Rapini or broccoli rabe (/ r ɑː b /) is a green cruciferous vegetable, with the leaves, buds, and stems all being edible;. And Sinapis alba L.) was examined over 2 years.In each year, ten genotypes from each species were evaluated with late season insects controlled with either methyl parathion or endosulfan. Species were first introduced in Canada, plant breeders have developed many more varieties.
Meanwhile, 29 and Hsp70 genes were explored in B. These are often grown in Canterbury for seed.

Population Structure And Phylogenetic Relationships In A Diverse Panel Of Brassica Rapa L Abstract Europe Pmc

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris Sclerotinia Stem Rot Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks

Brassica Rapa Rape Go Botany
B Rapa のギャラリー

Plants Of A Normal Rapid Cycling Line Of B Rapa Right And The Download Scientific Diagram
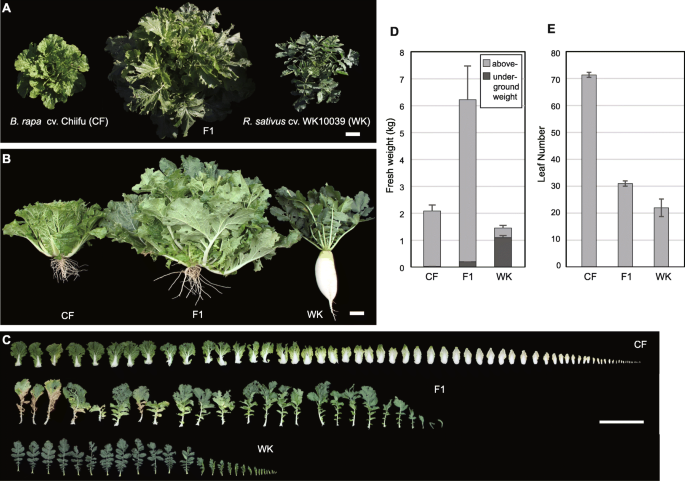
Revealing Biomass Heterosis In The Allodiploid X Brassicoraphanus A Hybrid Between Brassica Rapa And Raphanus Sativus Through Integrated Transcriptome And Metabolites Analysis Bmc Plant Biology Full Text
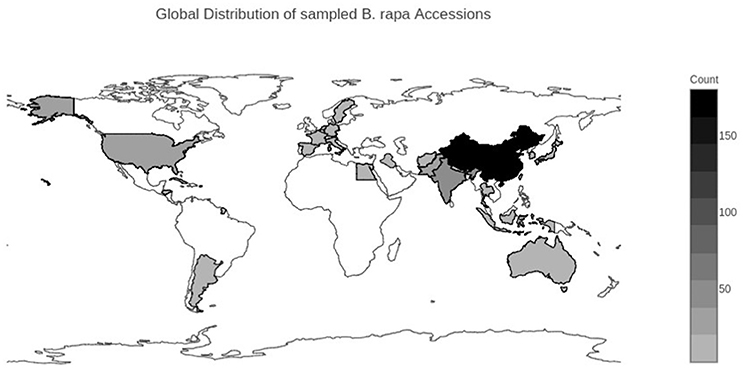
Frontiers Population Structure And Phylogenetic Relationships In A Diverse Panel Of Brassica Rapa L Plant Science
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqgf9btzs0qswktfwplttofl2anqmqteqx4cfv4m2 Qgp6nfiiu Usqp Cau

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris Black Leg Phoma Stem Canker Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks
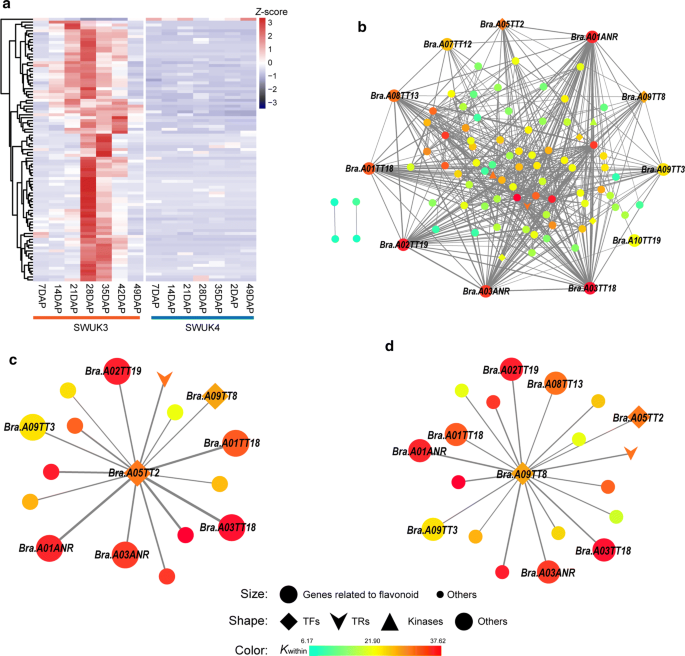
Deciphering The Transcriptional Regulatory Networks That Control Size Color And Oil Content In Brassica Rapa Seeds Biotechnology For Biofuels Full Text

Polymorphism Identification And Improved Genome Annotation Of Brassica Rapa Through Deep Rna Sequencing G3 Genes Genomes Genetics
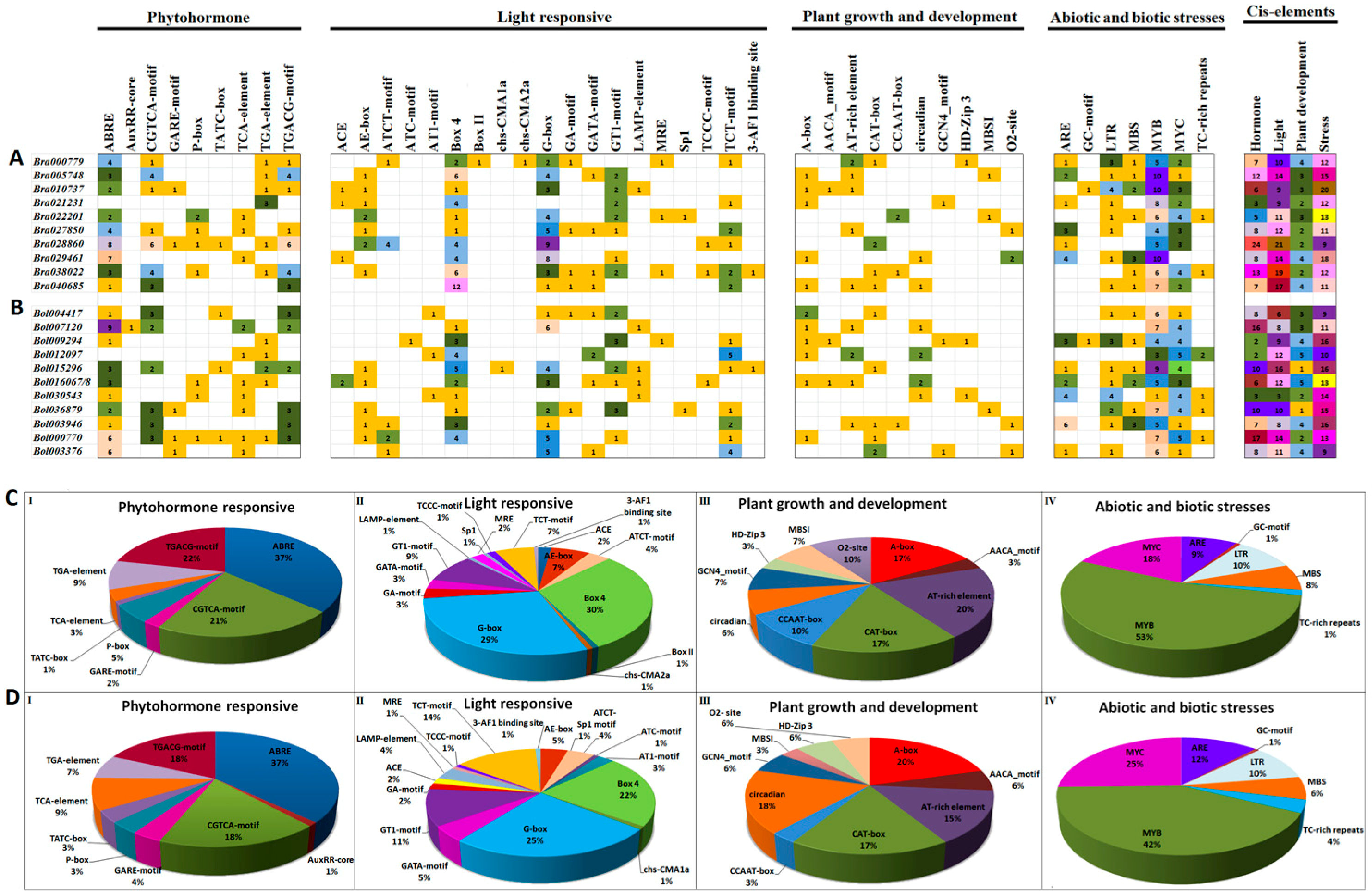
Genes Free Full Text Comprehensive Genomic Survey Characterization And Expression Analysis Of The Hect Gene Family In Brassica Rapa L And Brassica Oleracea L Html
A Large Insertion In Bhlh Transcription Factor Brtt8 Resulting In Yellow Seed Coat In Brassica Rapa

Brassica Rapa Rape Go Botany

Flower Morphology Of Left To Right B Rapa 1 Plant And F 1 H 6 Download Scientific Diagram

Genetic Dissection Of Leaf Development In Brassica Rapa Using A Genetical Genomics Approach Plant Physiology

A Leaf Morphology Of Left To Right Brassica Rapa Erucastrum Download Scientific Diagram

Brassica Rapa Wikipedia

White Rust Infection On B Rapa A Leaves B Flowers Download Scientific Diagram

Genetic Characterization Of Brassica Rapa Chinensis L B Rapa Parachinensis L H Bailey Hanelt And B Oleracea Alboglabra L H Bailey Hanelt Using Simple Sequence Repeat Markers

Brassica Rapa Lab Report

Effects Of Slug Herbivory On Seedling Recruitment In Brassica Napus And B Rapa Leiden University

Brassica Rapa Campestris Wild Turnip Pfaf Plant Database
Metabolic Profiling Of B Rapa R Sativus And The Hybrid 1 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Rave Sauvage Brassica Rapa Subsp Campestris L Clapham En Suisse Ressources Genetiques Dans Le Genre Brassica L Pour La Suisse Etude De Cas

Genetic Dissection Of Leaf Development In Brassica Rapa Using A Genetical Genomics Approach Plant Physiology

Nue In Oilseed Rape

Frontiers Association Of Micrornas With Types Of Leaf Curvature In Brassica Rapa Plant Science

Allelic Polymorphism Of Gigantea Is Responsible For Naturally Occurring Variation In Circadian Period In Brassica Rapa Pnas
3

B Rapa High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

B Rapa Versus A Thaliana Cogepedia
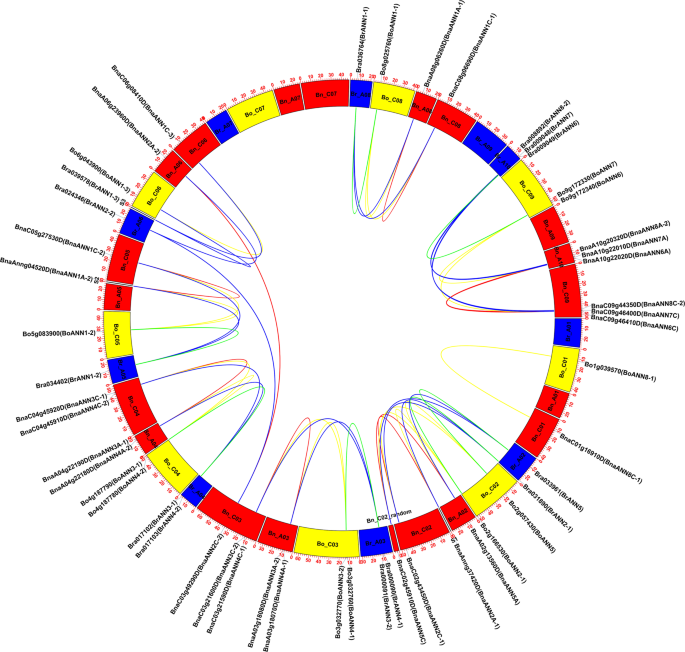
Comprehensive Analyses Of The Annexin Ann Gene Family In Brassica Rapa Brassica Oleracea And Brassica Napus Reveals Their Roles In Stress Response Scientific Reports

Chinese Cabbage Brassica Rapa Ssp Pekinensis A Valuable Source Of Resistance To Clubroot Plasmodiophora Brassicae Springerlink

Perk Gene Duplication Among B Rapa And A Thaliana B Nigra Download Scientific Diagram
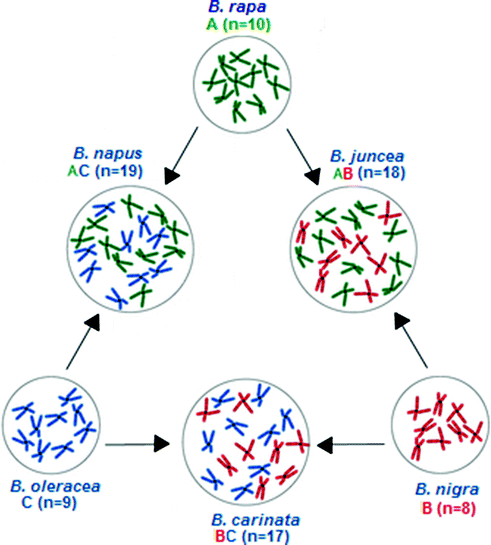
Economic Academic Importance Of Brassica Rapa Springerlink

B Rapa Genotype R O 18 Plant Development A Seedling Three Weeks Download Scientific Diagram

B Rapa High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
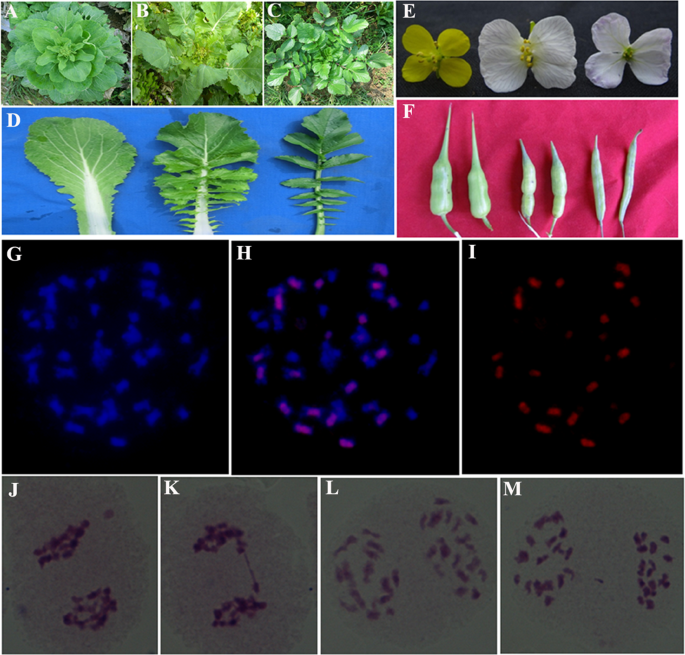

Integration Of Metabolome And Transcriptome Reveals Flavonoid Accumulation In The Intergeneric Hybrid Between Brassica Rapa And Raphanus Sativus Scientific Reports
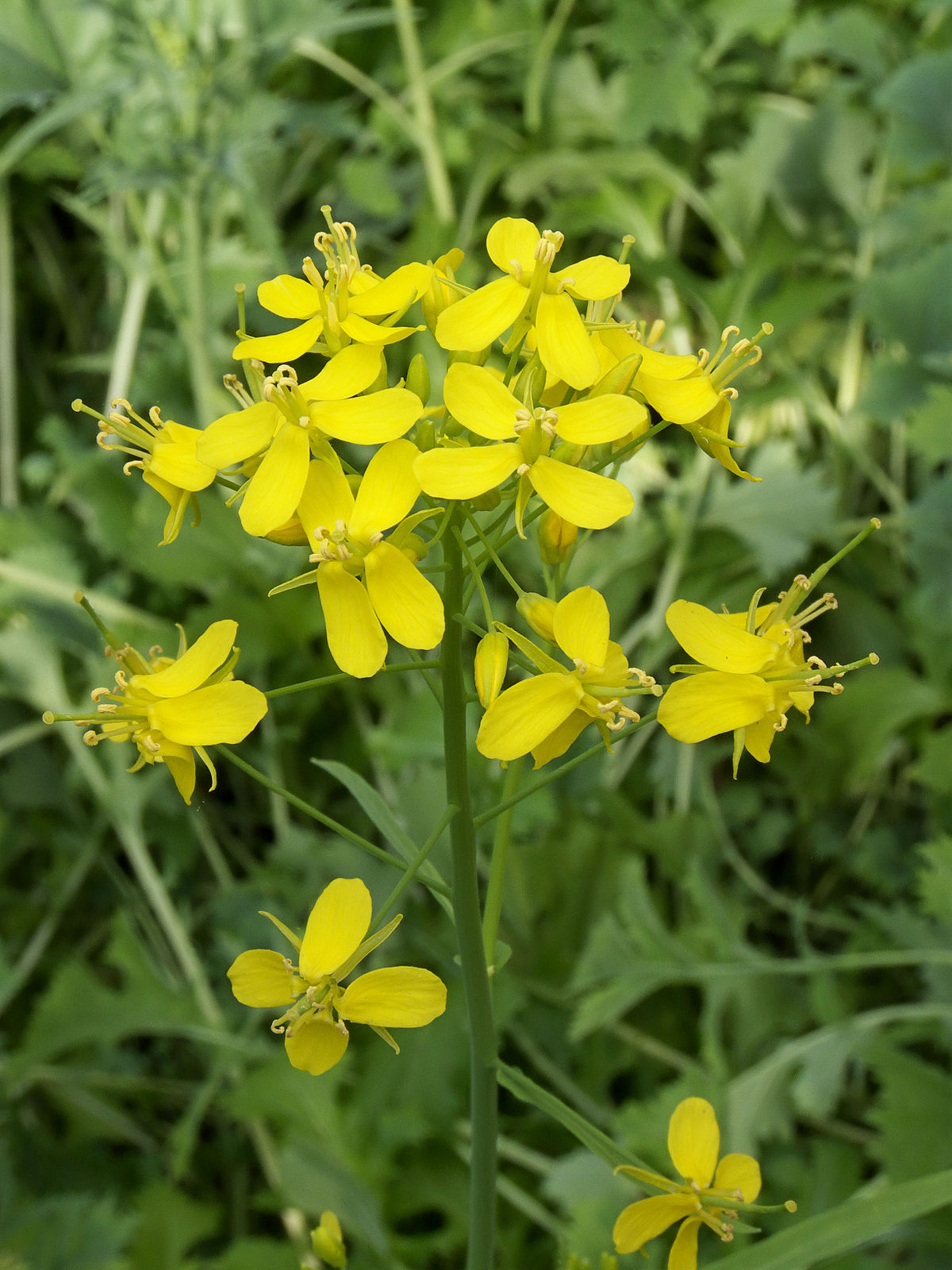

File Brassica Rapa Subsp Campestris Raapstelen Bloeiwijze 3 Jpg Wikimedia Commons

Alexander Descubes Mauritian Born Ca 1840 19 276 Brassica Camp Arader Galleries

B Rapa Genotype R O 18 Plant Development A Seedling Three Weeks Download Scientific Diagram

A Simple And Efficient Agrobacterium Mediated Transient Expression System To Dissect Molecular Processes In Brassica Rapa And Brassica Napus Mooney Plant Direct Wiley Online Library

Habit Of Three Species Of Brassica L A B B Rapa Subsp Campestris Download Scientific Diagram
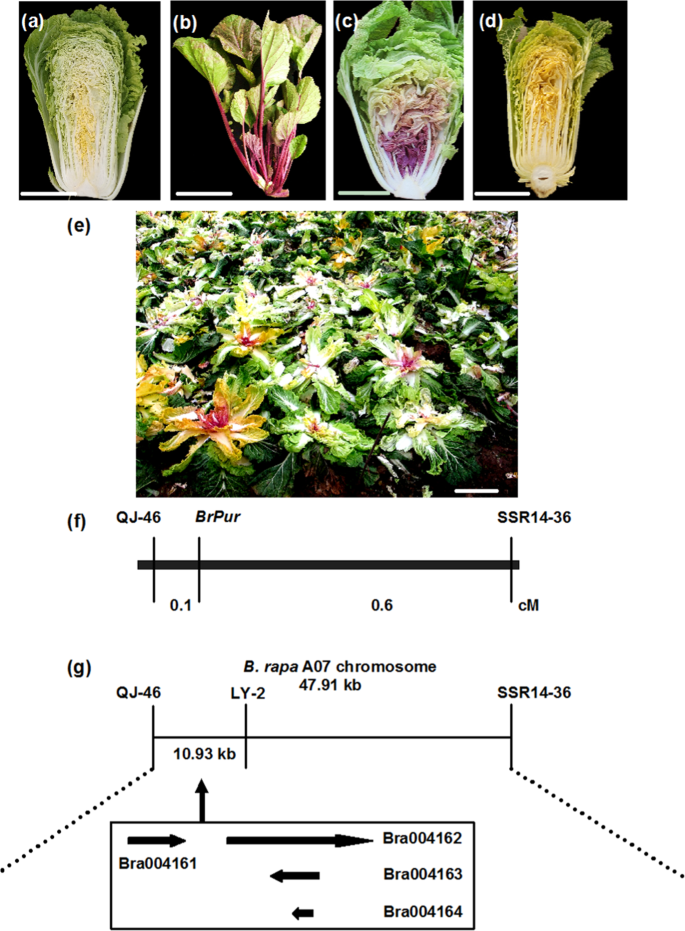
The Novel Gene Brmyb2 Located On Chromosome A07 With A Short Intron 1 Controls The Purple Head Trait Of Chinese Cabbage Brassica Rapa L Horticulture Research
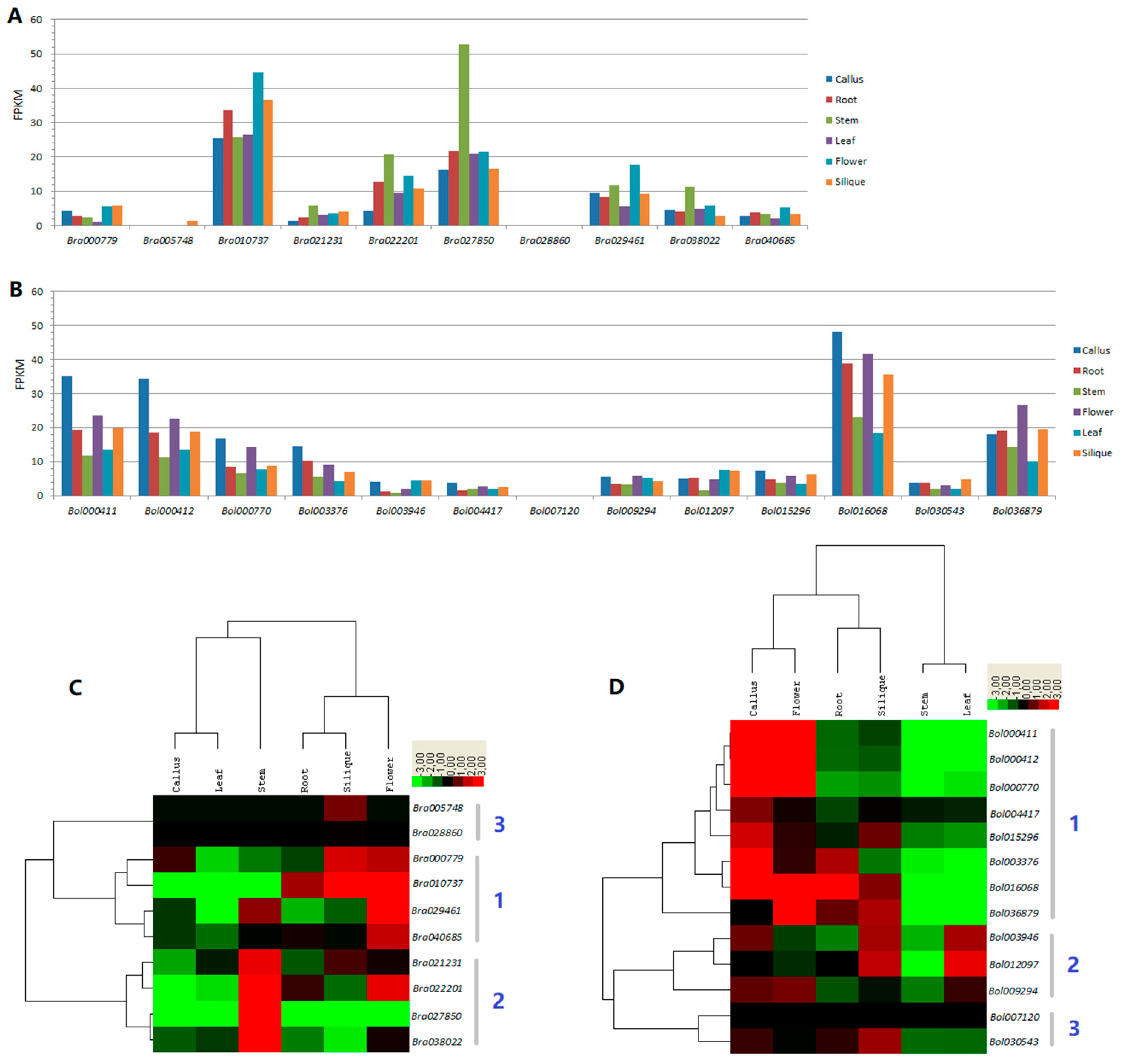
Genes Free Full Text Comprehensive Genomic Survey Characterization And Expression Analysis Of The Hect Gene Family In Brassica Rapa L And Brassica Oleracea L Html
Genes Free Full Text Brexlb1 A Brassica Rapa Expansin Like B1 Gene Is Associated With Root Development Drought Stress Response And Seed Germination

Category Brassica Rapa Subsp Chinensis Wikimedia Commons

Height To The Shoot Apex Of Normal Rapid Cycling B Rapa El And The Download Scientific Diagram

Establishment Of Kasp Marker Library For Genetic Diversity Analysis In Brassica Rapa Crops

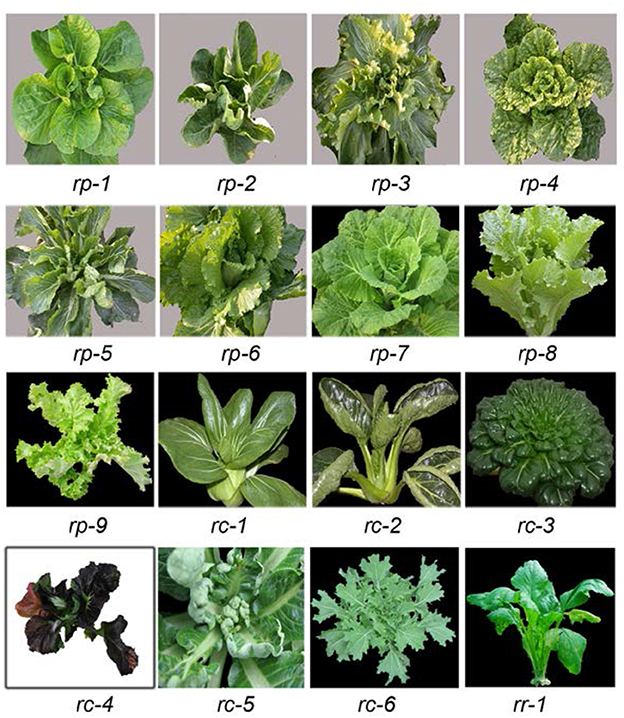
Diversity Of Leaf Curvature In B Rapa Rp 1 Through Rp 9 Are Nine Download Scientific Diagram

Brassica Rapa Edible Plants Edible Wild Plants Plants
B Rapa Fast Plant Presentation By Nicole Bermudez
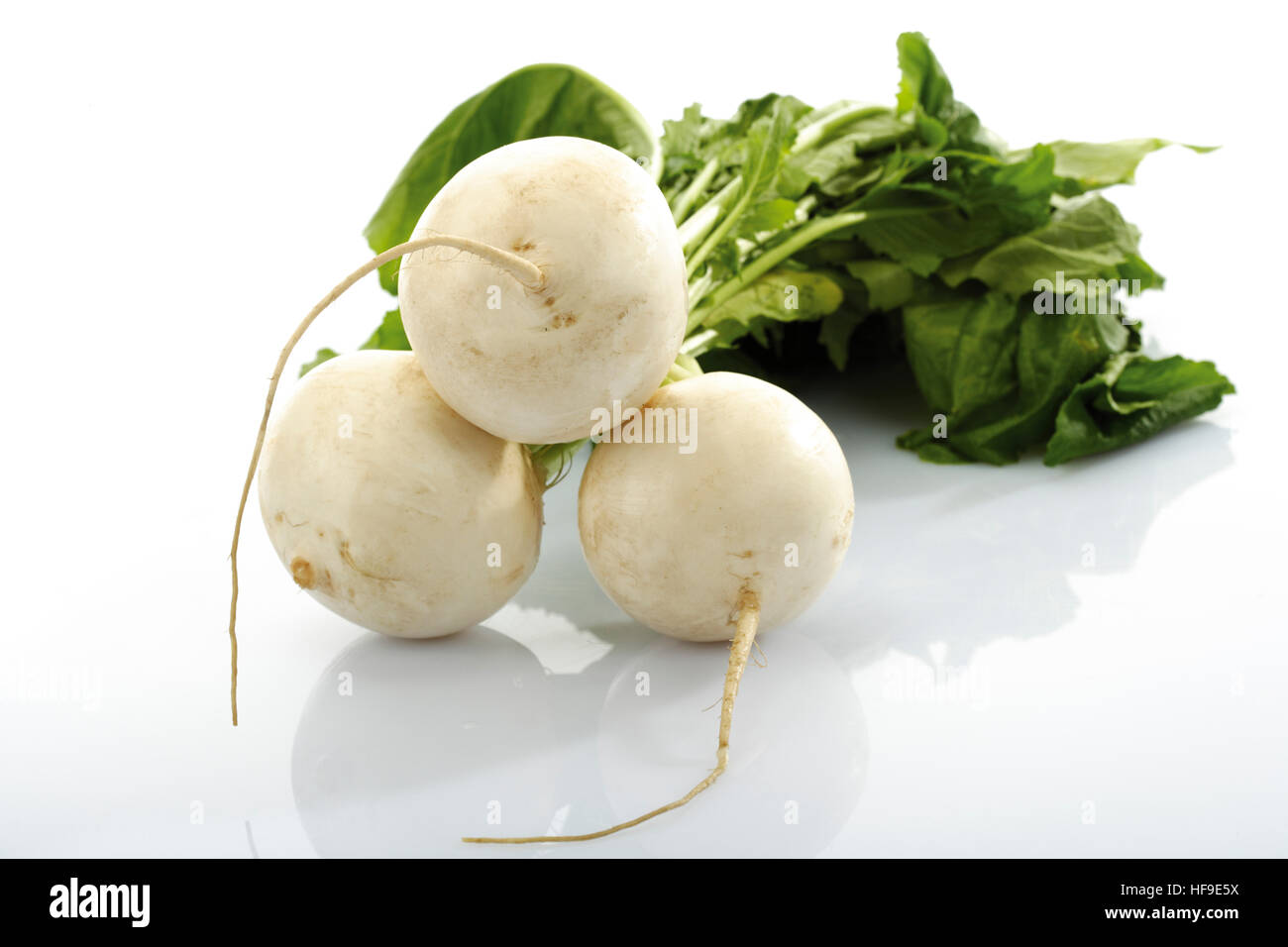

Turnips Brassica Rapa Var Rapa Stock Photo Alamy

Brassica Rapa Flower Structure A Schematic Longitudinal Section Of Download Scientific Diagram

Genomic Inferences Of Domestication Events Are Corroborated By Written Records In Brassica Rapa Biorxiv

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris White Leaf Spot And Gray Stem Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks
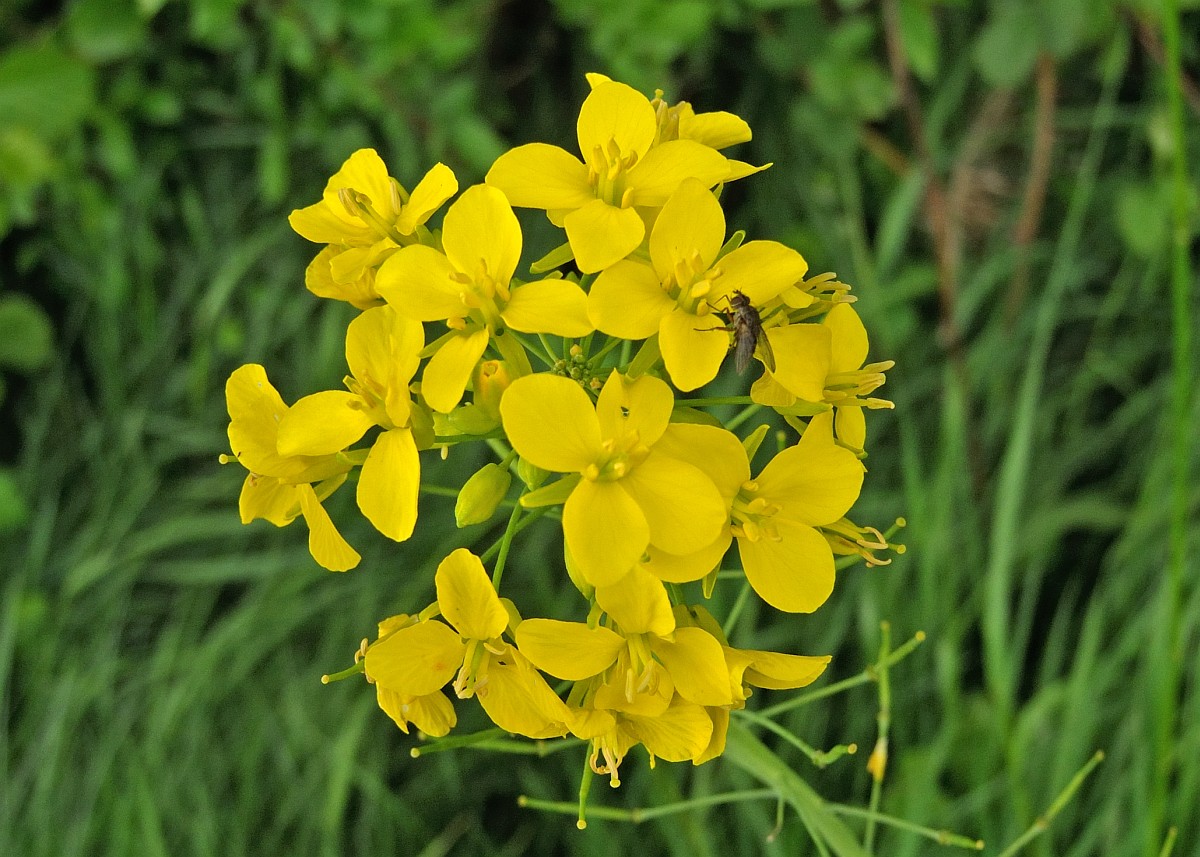

Brassica Rapa Wild Turnip

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris Black Leg Phoma Stem Canker Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks

Brassica Rapa Brukev Repak Pladias Database Of The Czech Flora And Vegetation

Brassica Rapa Manual Of The Alien Plants Of Belgium

Wild Plants Of Malta Plant Family Index
Characteristics Analysis Of F1 Hybrids Between Genetically Modified Brassica Napus And B Rapa

Polish Rapeseed B Rapa Albert Lea Seed Albert Lea Seed

Brassica Rapa Health Effects And Herbal Facts
Q Tbn 3aand9gcssjlojhxqlc1oqf2i4g Puldrbb4jtpz3wpuzyhmwi6qmj 6ww Usqp Cau

File Phylogenetic Tree Of R Sativus A Thaliana A Lyrata B Rapa And C Papaya Jpg Wikimedia Commons
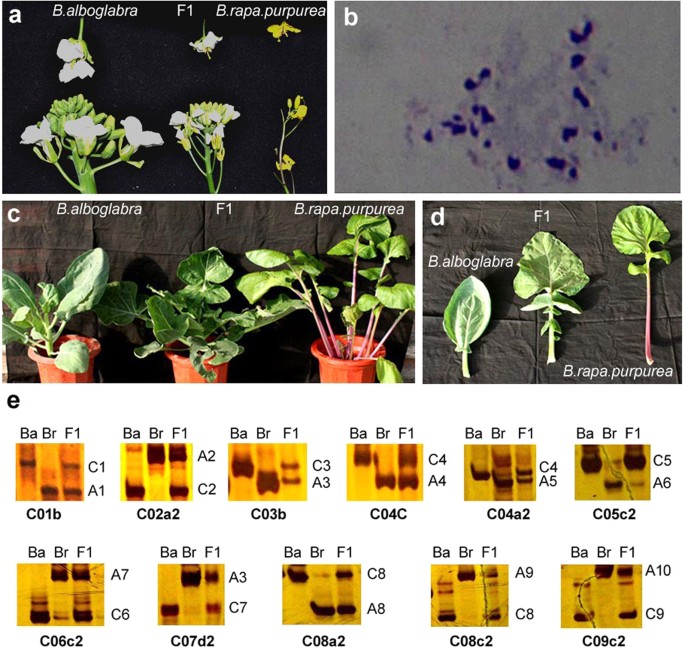
Interspecific Hybridization Polyploidization And Backcross Of Brassica Oleracea Var Alboglabra With B Rapa Var Purpurea Morphologically Recapitulate The Evolution Of Brassica Vegetables Scientific Reports
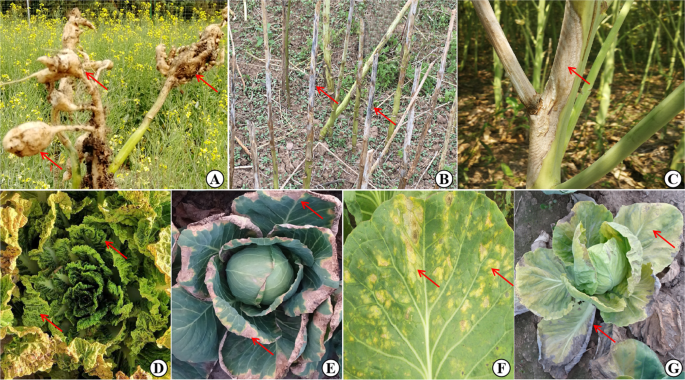
An Update On The Arsenal Mining Resistance Genes For Disease Management Of Brassica Crops In The Genomic Era Horticulture Research

Brassica Rapa Rape Go Botany

Genome Wide Identification And Expression Profiling Of Annexins In Brassica Rapa And Their Phylogenetic Sequence Comparison With B Juncea And A Thaliana Annexins Sciencedirect

Reconstruction Of The Brassica Rapa Ancestral Genome Plant Cell

Pollen Tube Growth From The Pollen Grains Of The B Rapa Transgenic Download Scientific Diagram

What S Blooming Now Field Mustard Brassica Rapa

Identification Of Functional Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Affecting Leaf Hair Number In Brassica Rapa Plant Physiology

Brassica Rapa Rape Go Botany
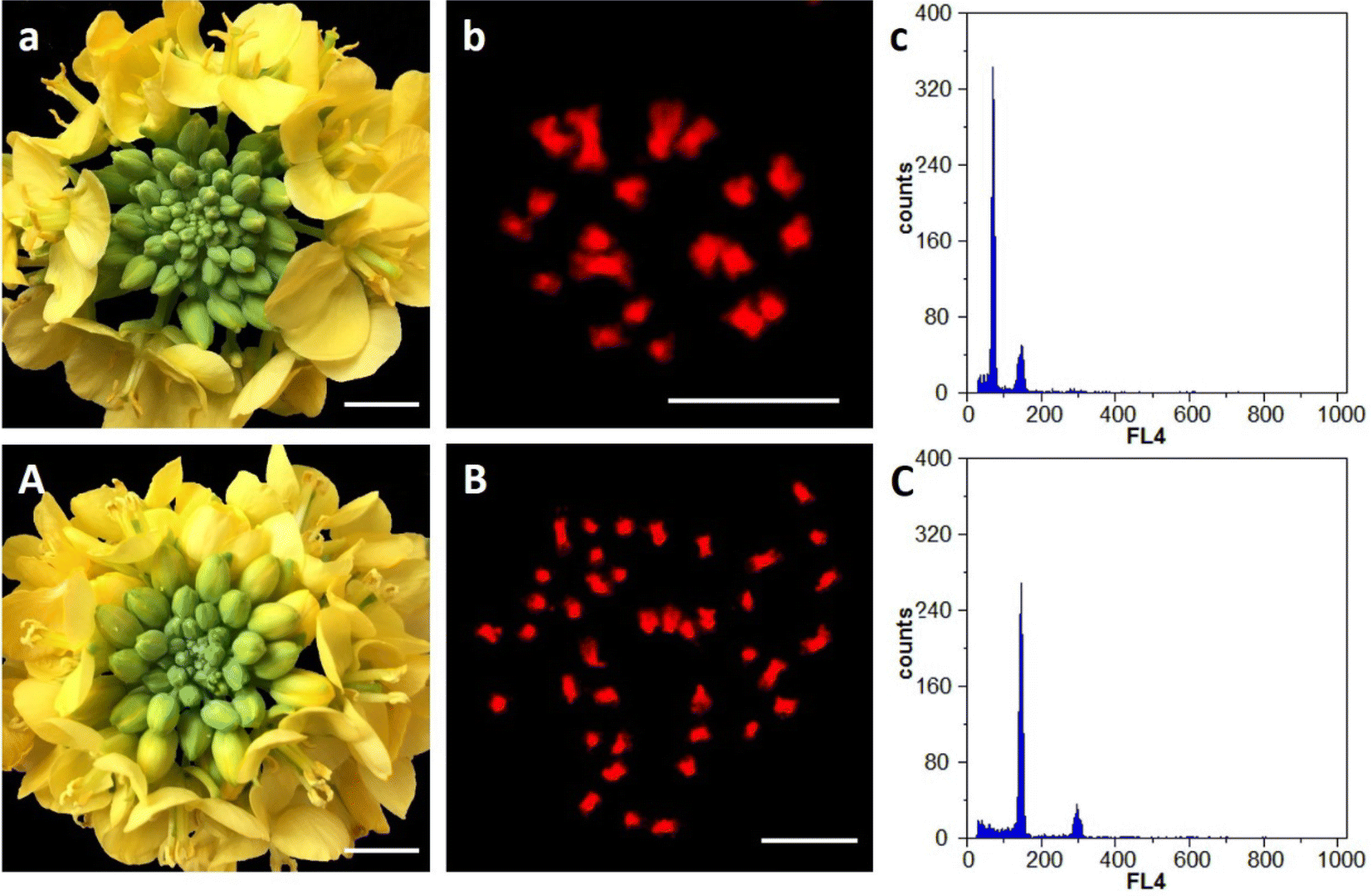
Cytological And Proteomic Analyses Of Floral Buds Reveal An Altered Atlas Of Meiosis In Autopolyploid Brassica Rapa Cell Bioscience Full Text

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris Black Leg Phoma Stem Canker Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks

Brassica Rapa Rape Go Botany

Genome Wide Identification And Characterization Of The Hsp70 Gene Family In Allopolyploid Rapeseed Brassica Napus L Compared With Its Diploid Progenitors Peerj

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris Sclerotinia Stem Rot Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks
Http Gutengroup Mcb Arizona Edu Wp Content Uploads Mec Pdf

Rich Morphotypes Of Brassica Plants A Morphotypes Of B Rapa Top Download Scientific Diagram

B Rapa High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Morphology And Cytology Of Flower Chimeras In Hybrids Of Brassica Carinata Brassica Rapa Semantic Scholar

Figure 2 From Transmission And Detection Of Toria Brassica Rapa L Subsp Dichotoma Roxb Phyllody Phytoplasma And Identification Of A Potential Vector Semantic Scholar

Genome Resequencing And Comparative Variome Analysis In A Brassica Rapa And Brassica Oleracea Collection Scientific Data

Figure 2 Production And Genetic Analyses Of Novel Brassica Rapa L Introgressions From Interspecific Crosses With Brassica Juncea L Landraces Native To The Qinghai Tibet Plateau Springerlink

A Sub Network Of The Predicted Interactome Formed By Putative B Rapa Download Scientific Diagram

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris Chlorotic Leaf Spot Light Leaf Spot Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks
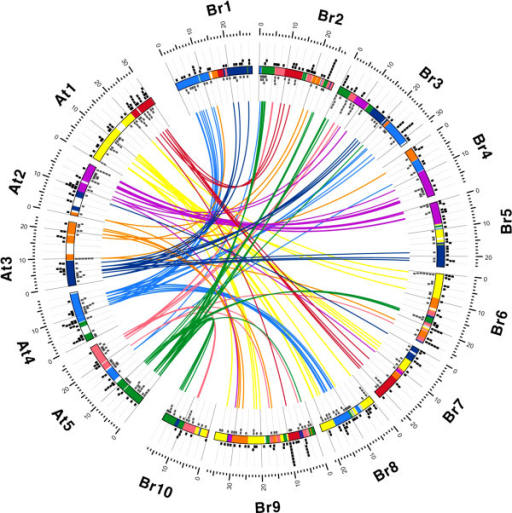
Circos Diagram Of Mirna Gene Pairs Between B Rapa And Open I

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris White Leaf Spot And Gray Stem Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks
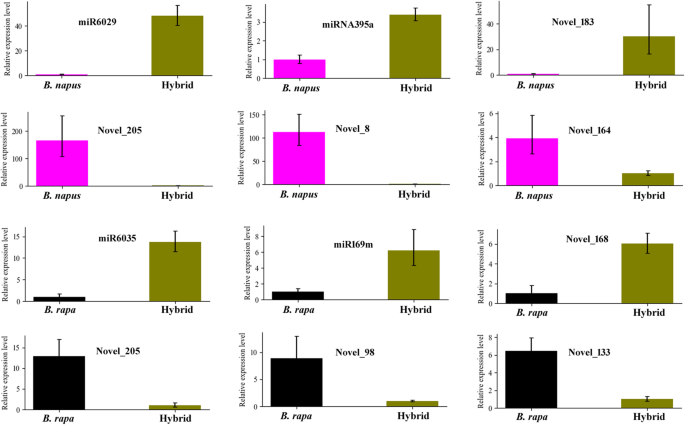
Characterization And Expression Profiles Of Mirnas In The Triploid Hybrids Of Brassica Napus And Brassica Rapa Bmc Genomics Full Text

Distribution Of Genomic Blocks Along Ten Chromosomes Of The B Rapa Download Scientific Diagram

Rapid Cycling Brassica Types Crop Production

Mean Sd Of Dry Weight Of B Rapa Roots N 15 Five Plants Per Plot Download Scientific Diagram
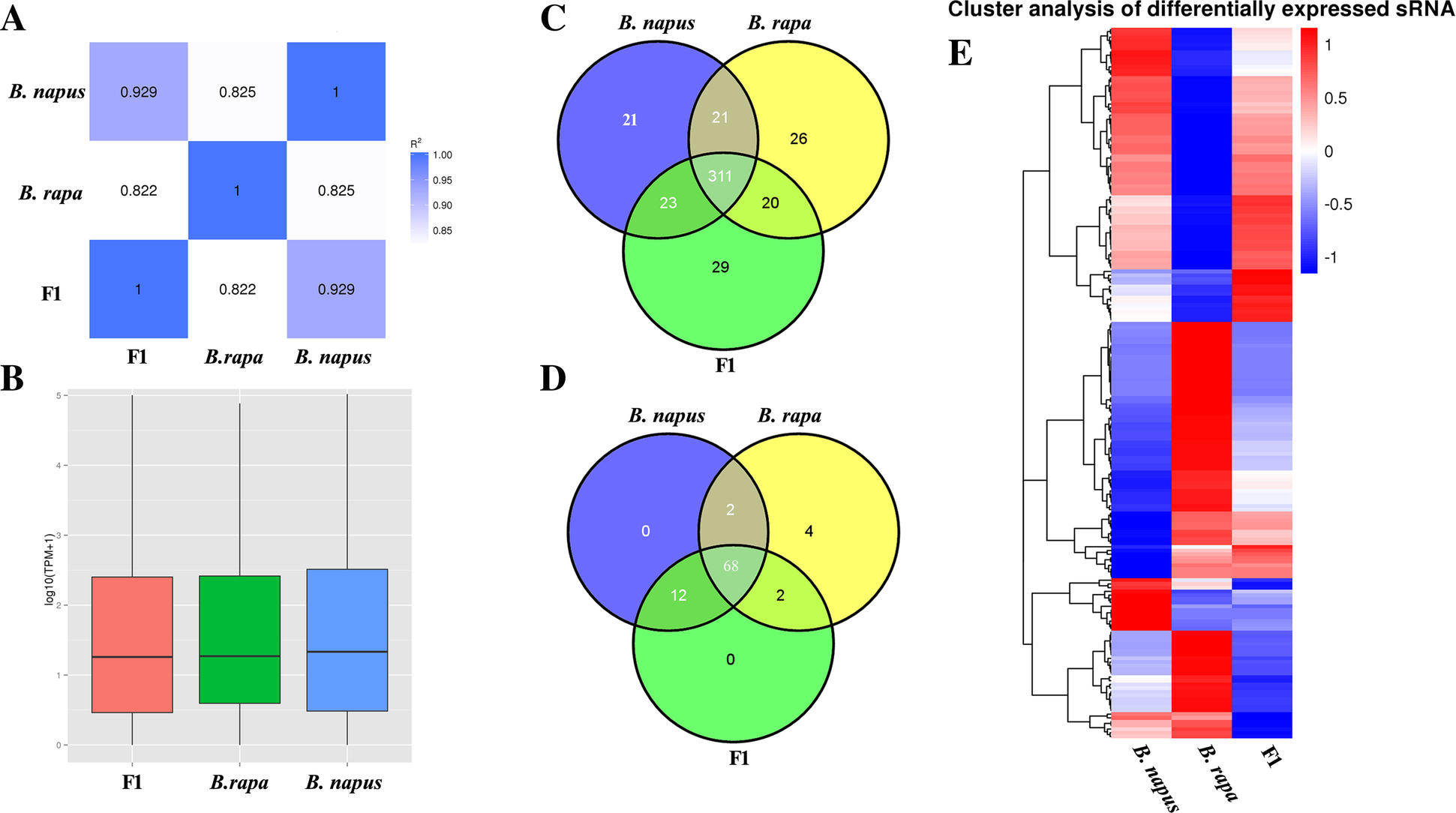
Characterization And Expression Profiles Of Mirnas In The Triploid Hybrids Of Brassica Napus And Brassica Rapa Bmc Genomics Full Text
Plos One Genome Wide Identification And Role Of Mkk And Mpk Gene Families In Clubroot Resistance Of Brassica Rapa

Brassica Rapa Field Mustard Discover Life Mobile

Rapeseed Canola Brassica Napus And B Rapa B Campestris White Leaf Spot And Gray Stem Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks

Flowers Of Wild Type And Mutant B Rapa And B Napus A L B Rapa Download Scientific Diagram

Brassica Rapa Wildflowers In Santa Barbara
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqxrsnihwq7uttzow1srgvl8pdvhhye7el7u Vwooi Usqp Cau

Plants Of Original B Napus Cv Vikros And Its Mutant Progeny Plants Download Scientific Diagram

Genetic Dissection Of Leaf Development In Brassica Rapa Using A Genetical Genomics Approach Plant Physiology



